|
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_respiration
|
|
|
What is biochemical energy from nutrients converted into?
|
|
|
How many ATP are produced during cell respiration as a whole?
|
|
|
Why are respiration reactions called catabolic?
|
|
|
What is an anabolic reaction?
|
|
|
Why is cellular respiration considered a redox reaction?
|
|
|
What oxidizing agent is used in the redox reactions of respiration?
|
|
|
What processes are driven by ATPs?
|
|
|
How is most ATP made?
|
|
|
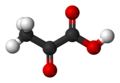 What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H) What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H)
|
|
|
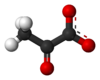 What is it? What is it received from? Through oxidation or reduction? What is it? What is it received from? Through oxidation or reduction?
|
|
|
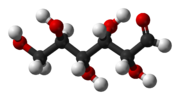 What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H) What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H)
|
|
|
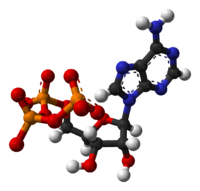 What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H, the orange are P, the blue are N) What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H, the orange are P, the blue are N)
|
|
|
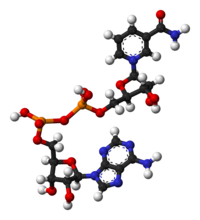 What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H, the orange are P, the blue are N) What is it? ( the black are C, the red are O, the white are H, the orange are P, the blue are N)
|
|
|
What part of ATP gets unhooked from it to transpher energy?
|
|
|
What does ATP get transformed into?
|
|
|
Where does a phosphate-oxygen group get attached to ADP again?
|
|
|
What are the 4 main stages of cell respiration?
|
|
|
Where does glycolysis take place?
|
|
|
What is produced as a result of glycolysis in aerobic conditions?
|
|
|
What is produced as a result of glycolysis in anaerobic conditions?
|
|
|
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8Kn6BVGqKd8
|
|
|
How many stages does glycolysis comprise?
|
|
|
How many ATPs are produced in the process of glycolisis?Why not 2?
|
|
|
Why is the net ammount of ATP still 2 but not 4?
|
|
|
What facilitates the reactions in glycolysis?
|
|
|
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cellular_respiration
|
|
Where does oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate take place?
|
|
|
|
|
|
How many percent of energy produced in a mitochondrion of a modern cell did glycolysis provide?
|
|
|
What allowed increasing the amount of energy production in a cell?
|
|
|
Where is the Krebs cycle started
|
|
|
Why is decarboxylation called oxidative?
|
|
|
What happens to these electrons?
|
|
|
At what stages is the second NADH energy carrier is made?
|
|
|
What is useless matter produced in the Krebs cycle?
|
|
|
What is useful energy?
|
|
|
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lRlTBRPv6xM
|
|
|
Where do electrons move in a bacterial cell?
|
|
|
How do they get there?
|
|
|
What molecule accepts electrons at the end of the electron transport chain? From what?
|
|
|
What is formed?
|
|
|
The gradient of what cations increases outside the cell membrane?
|
|
|
How does it affect the pH of the outside of the cell?
|
|
|
Do none of electron carrying proteins accept protons?
|
|
|
How does coenzyme Q influence the proton gradient and the proton mode of force.
|
|
|
http://www.trueorigin.org/atp.asp
|
|
|
What is the difference between Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic ATP production?
|
|
|
What falsifies Darwin’s theory of evolution?
|
|